Responsible AI: Shaping a Better Future Together
Harnessing the power of AI responsibly to create a more ethical, transparent, and brilliant future for us all.
The Pillars of Responsible AI

Safety
Ensuring AI systems are secure and do not pose risks to humans or society.

Fairness
Developing AI that treats all individuals and groups equitably, without bias or discrimination.
Transparency
Creating AI systems that are explainable and open to scrutiny.

Accountability
Establishing clear responsibility for AI decisions and their consequences.
Ethical Considerations in AI Development
Of course, there are many ethical considerations when developing AI models, however the main considerations are detailed below:
Transparency in AI Decision-Making
Explainable AI (XAI)
Developing AI models that can provide clear explanations for their decisions and actions.
Algorithmic Audits
Conducting regular audits of AI systems to ensure compliance with ethical standards.
Open-Source Initiatives
Promoting transparency through open-source AI projects and collaborative development.
Public Engagement
Involving diverse stakeholders in the development and deployment of AI technologies.
Blockchain Verification
Leveraging blockchain’s immutable nature to ensure AI aligns with principles like responsibility, robustness, interpretability, ethics, and auditability. This enhances transparency, security, and regulatory compliance.
There’s more to Responsible AI than just responsibility
Responsible AI
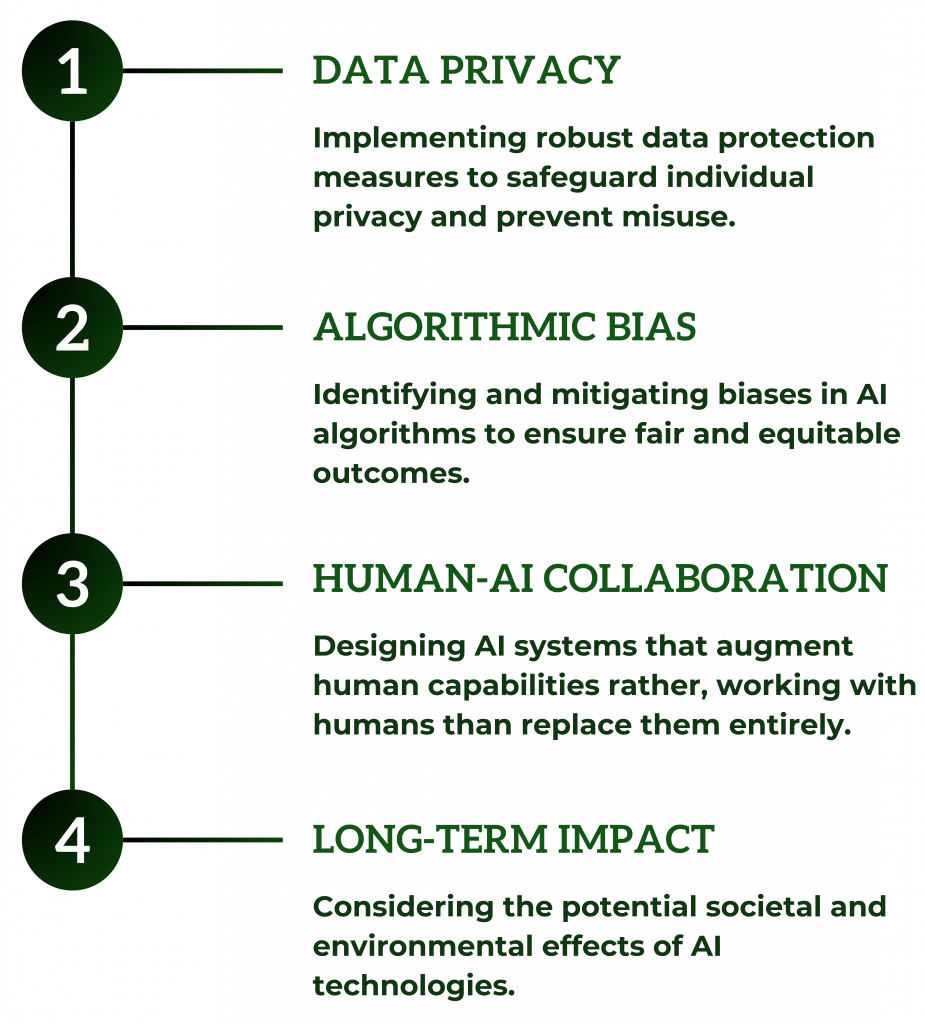
Responsible AI involves designing and deploying artificial intelligence systems in a manner that prioritizes safety, fairness, and accountability. This includes addressing potential biases, ensuring that AI systems respect user privacy, and making decisions that align with societal values and ethical standards.
Robust AI
Robust AI focuses on creating systems that perform reliably under a variety of conditions and can withstand adversarial attacks or unexpected inputs. This involves thorough testing and validation processes to ensure AI systems are resilient, secure, and capable of maintaining their functionality over time.
Ethical AI
Ethical AI ensures that AI technologies are developed and used in ways that adhere to ethical guidelines and principles. This includes promoting fairness, avoiding harm, and ensuring that AI contributes positively to society. Ethical AI also involves continuous monitoring to mitigate unintended consequences and negative impacts.
Interpretable AI
Interpretable AI aims to develop models and algorithms that provide clear and understandable insights into their decision-making processes. This transparency helps users and stakeholders trust AI systems by making it easier to understand how and why specific outcomes are reached.
Auditable AI
Auditable AI emphasizes the importance of maintaining detailed records and documentation of AI systems’ development, deployment, and operation. This allows for regular reviews and audits to verify compliance with regulatory standards, identify and address issues, and ensure transparency and accountability throughout the AI lifecycle.
AI Safety and Security Measures
Robust Testing
Implementing rigorous testing protocols to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Continuous Monitoring
Establishing real-time monitoring systems to detect and respond to anomalies and unexpected actions.
Fail-Safe Mechanisms
Designing Al systems with built-in safeguards to prevent unintended harmful actions.
Ethical Hacking
Employing ethical hackers to identify and address potential security vulnerabilities.
Return to TAFU’s Responsible AI Hub.
